In 2021, McKinsey reported that 71% of customers in the new age prefer personalized content and interactions during their shopping interactions online.. Over 6 in 10 companies aim to move to headless commerce in 2024, with the concept itself estimated to grow to a $32 billion dollar industry by 2027. Traditional e-commerce platforms, with their monolithic architecture, often struggle to keep pace with the rapidly changing demands of the digital marketplace. This has led to the emergence of headless and composable commerce as the next generation of e-commerce solutions.
Understanding Headless Commerce
Headless commerce refers to the decoupling of the front-end presentation layer from the back-end commerce functionality. This separation allows for greater flexibility in how content is delivered to users, enabling businesses to leverage various front-end technologies to create unique customer experiences.
The benefits of this approach are manifold. By decoupling the front-end and back-end, businesses can update their user interface without impacting the underlying commerce logic. This leads to faster iteration and innovation cycles. Additionally, headless commerce facilitates omnichannel retailing, allowing businesses to deliver consistent experiences across various touchpoints.
The rise of APIs and microservices, as technological advancements, have facilitated the adoption of headless commerce. These technologies enable the seamless integration of different systems and services, allowing businesses to build a best-of-breed commerce stack.
Composable Commerce: Improving On Headless Commerce

Composable commerce takes headless commerce a step further by introducing a modular approach to building e-commerce solutions. It emphasizes the use of packaged business capabilities (PBCs), which are self-contained units of functionality that can be independently deployed and managed.
The MACH architecture (Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, and Headless) plays a crucial role in enabling composable commerce. It provides a framework for building flexible and scalable commerce platforms that can adapt to changing business needs.
The advantages of composable commerce are significant. It offers businesses the ability to mix and match different PBCs to create a customized commerce solution that fits their unique requirements. This modularity also makes it easier to integrate new technologies and respond to market trends.
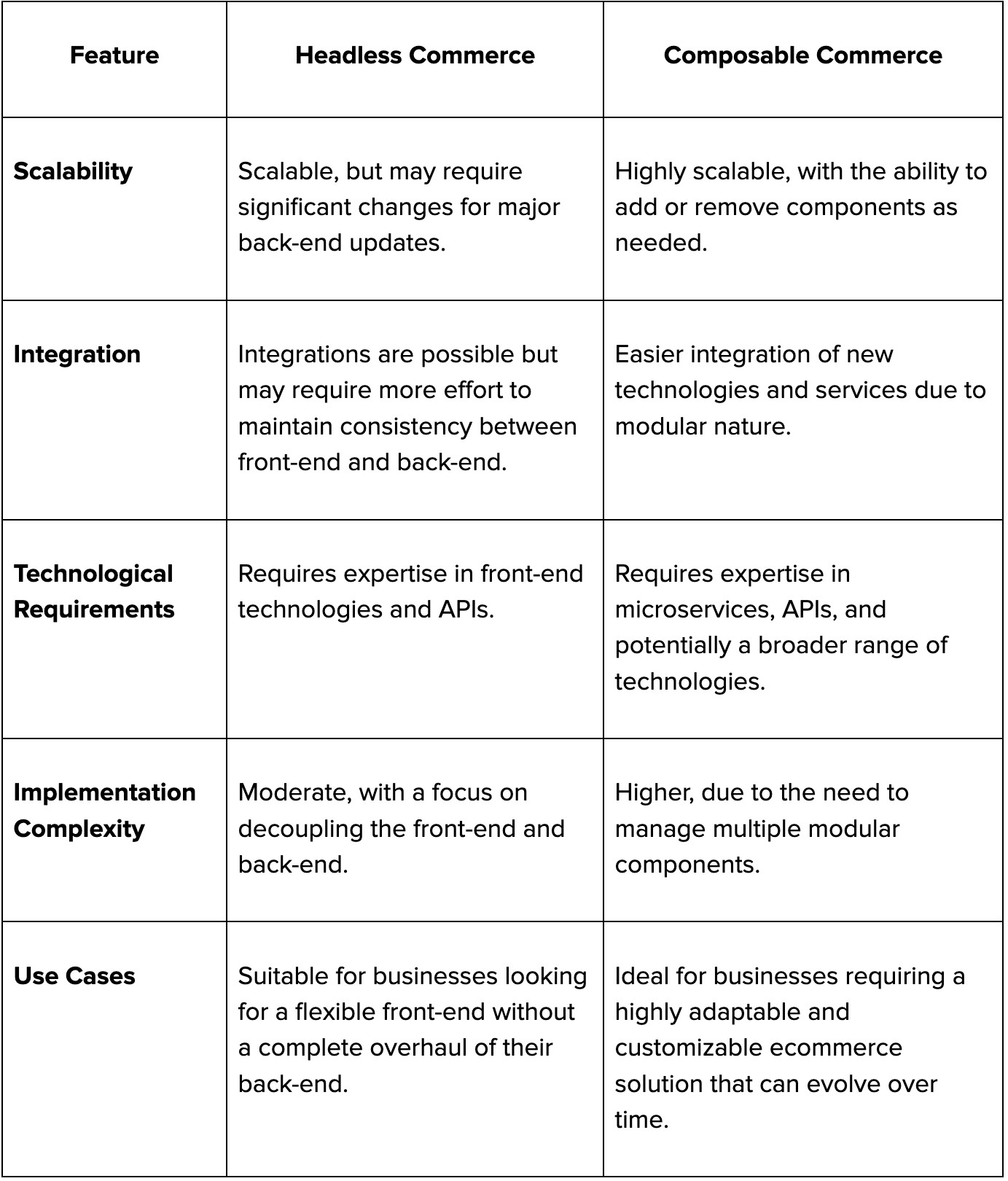
Key Differences Between Headless and Composable Commerce

While both headless and composable commerce offer flexibility and customization, there are key differences between the two. Headless commerce focuses primarily on the separation of the front-end and back-end, whereas composable commerce extends this concept to the entire commerce stack.
Composable commerce offers a higher degree of customization and scalability due to its modular nature. It also provides better integration capabilities, as businesses can easily add or replace PBCs without disrupting the entire system.
A detailed table with the core differences between headless commerce and composable commerce is given below.
The Significance of Microservices and PBCs
The architecture of composable commerce fundamentally relies on microservices and PBCs. While microservices are small, independently deployable services that make up a larger application, PBCs are more business-focused, encapsulating specific commerce functionalities.
The distinction between microservices and PBCs lies in their granularity and purpose. Microservices are more technical and can be used to build various applications, while PBCs are tailored to specific business needs in the commerce domain.
Why Businesses Are Adopting Composable Commerce

Alt text: Why Businesses Are Adopting Composable Commerce
Businesses adopt composable commerce for its unparalleled flexibility, which enables them to quickly adapt to market changes and evolving customer demands. By leveraging packaged business capabilities (PBCs) and microservices, companies can easily customize their commerce platforms, integrate new technologies, and scale their operations as needed. This agility and customization potential make composable commerce an attractive option for businesses looking to stay competitive in the dynamic e-commerce landscape.
Prioritizing Qualities for Modular Business Success
For businesses looking to succeed with a modular commerce approach, prioritizing the adoption of the MACH architecture is crucial. This future-proofs their commerce solutions, ensuring they can easily integrate new technologies and respond to market changes.
Key development tools and APIs are essential for building custom technology stacks that meet specific business needs. Additionally, support and cross-vendor collaboration are important in composable ecosystems, as they enable businesses to leverage the collective expertise of different providers.
The Origins Of Modern Commerce Are Here To Stay
The shift from traditional e-commerce to headless and composable commerce reflects a fundamental change in how businesses approach digital commerce. Headless commerce's decoupling of the front-end and back-end allows for greater flexibility and omnichannel capabilities. Composable commerce takes this further by offering a modular approach to building e-commerce solutions, enabling businesses to customize their platforms with ease.
Omind is a CX and BX platform that leverages the best of industry knowledge, AI, ML and more proprietary prowess to help you engage in the best way possible. If you’d like to learn more about how you can augment your composable experience with us, schedule a demo at this link today.
AUTHOR
Team Omind
Empowering Businesses with Unified Customer Experience Platform, Leveraging Advanced AI and Intelligent Automation
PRODUCT
Unified CXM
Share LINK
Related Blogs